It is impossible to run a business without a customer. All goods and services are created by people and for people. If there is demand, there will be someone willing to fulfill it. In this article, we are going to discuss how to find your target audience, understand your customers, and use this information for business development.
What is the target audience and what should we know about it?
The target audience is people potentially interested in your goods or services. You should consider them when launching your business, designing the product and its packaging, and running other marketing activities.
They are the people with requirements and problems that your product might solve. At the same time, the real target audience is not always the same as the desired one. For example, a company produce unique tableware and plan to sell it at retail to those who are interested in design. But it turned out that restaurants were more interested in the product, and the company started receiving orders from all over the world. Thus, the real target audience is not retail customers but representatives of the restaurant trade.
You need to know your target audience to:
- Make a unique selling proposition;
- Determine sales channels;
- Cut down expenses on ineffective advertising;
- Increase customer loyalty;
- Personalize your communication with clients.
Knowing your target audience helps in:
- determining your business area
Also, it helps you understand what areas you are going to expand into. Goods are not produced for the sake of them. For example, if you sell mattresses for pets, you need to target dog and cat owners. Those who don’t have pets won’t be interested in your offer.
- analyzing your competitors
It is easier to track other companies in your industry if you know your target audience. “Borrowing” your competitors’ target audience for launching targeted advertising of your brand is standard practice.

- following trends
Change is all around us. The world evolves and so does your target audience. Businesses should be aware of the latest trends in the industry and be able to adapt to current needs.

- knowing and hearing your client
The avatar that you made once is not enough. You need to look into people’s core values. You need to find out what is important to your clients and how your product helps relieve certain pain points. It is also important to collect feedback to make adjustments to your promotion and selling strategy.

- avoiding wasting your budget
You will waste your budget if you launch an advertising campaign that is not aimed at your target audience. Even if you maximize your investments, there is a risk of getting low results. And it all happens, if you don’t target the right audience.
|
When you launch a new business, it may seem that the target audience is clear, and there is no need for market research. But researching and understanding your target audience is a complicated and in-depth process. The best option is to let professionals do it for you, but it wouldn’t hurt to know how to segment your target audience yourself. This knowledge will not only help you understand the market trajectory but also will be needed when you launch a traditional advertising campaign and set up targeted advertising. |
Types of the target audience
Major target audience
This is the highest priority group for brand communication. They are the people who are most likely to make purchases and are final decision-makers.
Minor target audience
They play a passive role during the decision-making process, but partially or fully influence people from the major group. They are not the priority of the company during advertising communication.
| Let’s review the children’s toy company LEGO as a simple example of the difference between major and minor target audiences. The company views kids as a priority when promoting the brand. They are their main audience, whom they target when launching advertising videos and campaigns. But kids cannot buy a LEGO set, so they ask their parents to do it. They influence the decision-making process, but the final decision is always made by a parent. For LEGO, they are their minor target audience. |

Wide target audience
This includes anyone interested in the product or service. It normally breaks down into several segments.
Narrow target audience
It is a group of people that have precise requirements for the product or service.
| For example, tea lovers are a wide target audience, but those who drink only Pu-Erh tea are a narrow target audience. Car owners are a wide target audience, but those who prefer a certain brand are a narrow target audience. |

Target audience characteristics
The characteristics of the target audience are the features that determine what segment people fall into, i.e. who they are, what is interesting and important for them, what values they share, how much they earn and spend, where they live, and who they spend time with.
Here are some of the main characteristics:
Geographic
It is one of the easiest and clearest characteristics of segmentation. Ad impressions depend on a person’s location. Geolocation allows spotting a potential client and offering them products or services required at that particular moment.
Thus, demand for sunscreens and bathing suits is higher at resorts, than in northern regions. Sometimes geolocation can be attached to a particular place. For example, a person who is passing a coffee shop is immediately shown targeted advertising for a discount in this shop.
| There are cases when it is not important to divide the target audience into narrow segments according to the geographic principle. For example, when you launch a large-scale campaign for the whole country. In other cases, it is better to specify the particular cities, neighborhoods, and addresses. |
It is a common practice among advertisers to use particular places in cities to address customers’ pain points and offer a solution.

Demographic
These are the parameters that define a person: gender, age, nationality, language, marital status, and having/not having children.
There are options for covering broader (by gender) or narrower segments (age, children, marital status, etc.). It all depends on how precisely you want to hit the target.
As a rule of thumb, these parameters are easy to analyze: on social networks people often indicate their year of birth, marital status, and other characteristics that help marketers to find the right people.
| An advert of a burger place, for example, is not good for audiences over 60, and a nail service most likely won’t be interesting for men. |

Socio-economic
Here the main criteria are the level of education, the field of professional activities, sources, and level of income. It directly influences purchasing power.
When people view an advert, they want to associate themselves with the characters of the campaign and share brand values. It means that the message should be clear, relevant, and should resonate with them. That is why products and services are always advertised by those people, who have generalized features of the main target audience.
| For example, it makes no sense to advertise expensive sports cars to a low-income audience. Training courses in the digital industry are more likely to be interesting for promotional specialists rather than for security guards. There is a high probability that pensioners will be buying medicine for lowering blood pressure and for controlling blood sugar. |
Not only geography, age, and income level influence the purchasing decision-making process but also a person’s values, personality type, and opinion also play an important role here.

Psychographic
It includes factors that are hard to analyze but that define a person: lifestyle, values, principles, dreams, fears, problems, idols. They are all “levers” that marketers use during the promotion.
It also comprises the amount of time to make a decision and the vision of the world. In this way, conservatives normally spend a long time thinking over the purchase and evaluating all the pros and cons. Creative people and impulsive people make purchases faster and are more receptive to marketing campaigns.
| Many purchases are influenced by positive emotions. If you know what makes your audience feel nostalgic and what associations with your product it may have, it will be easier to make a unique proposition and make customers interested. |
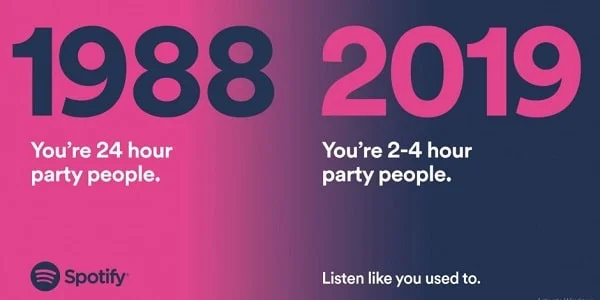
Moreover, quite often people want to feel that they belong to a certain group or associate themselves with their idol. That is why the products advertised by influencers sell so well.
Often brands reach out to celebrities to attract attention to serious problems.

Behavioral characteristics
This is about human behavior while making a choice, decision, purchase, and when using a product or a service.
Marketers need to understand what drives a person in each particular moment. Does it need to be a special occasion to buy a product or it is an everyday purchase? What do clients expect from the purchase and how fast do they need to solve a problem with the help of the product? Does a person value the price, customer’s service rate, prestige, or other parameters?
Customers’ attitude to a brand plays quite an important role as well. Customers fall under several categories:
- Devoted. They are not brand switchers, try out new products of the brand they have chosen.
- Loyal. They are familiar with the brand, use it, but sometimes prefer competitors.
- Little interested. They know about the brand but don’t use it.
- Uninterested. Don’t know about the brand and don’t use it.
| Each category needs a special approach. The easiest is to sell products to devoted and loyal customers. But it is also possible to win competitors’ customers over even if they are still not familiar with the brand. You just need to know your customer avatar and their pain points. |

Segmentation of the target audience according to the 5W method
Mark Sherrington, the founder of a big consulting corporation Added Value, suggested a simple and illustrative method for segmenting and determining your target audience. It is called 5W. It consists of 5 questions that should be answered by a business owner or a marketer before making a market proposition.

What? – your product
What do you produce and what do you offer to your customers? What products and services do they need?
Who? – your customer
Who is going to use your product? Who needs it?
When? – the right moment
In what situation would your client want to you use your products and services? When do your clients want it?
Where? – your distribution channel
Where your customers can see your offer? Where can they get the service?
Why? – motivation
Why do people need your service or product?
Due to this versatile method, you can analyze any business and find the audience that will be interested in it.
|
Let’s look at the example of an “on the go” coffee shop that is analyzed according to the 5W method: What? — coffee and hot non-alcoholic drinks “to go”. Who? — a trendy person from 18 to 40, who works nearby and is used to buying coffee on the way to work, as well as residents of the neighboring houses and random pedestrians. When? — most typically on workdays in the morning, before and after working hours. Where? — in the coffee shop itself, at the point-of-sale, in promotional leaflets, as well as through advertising targeted according to the location principle. The customers can get the product directly at the point-of-sale. Why? — qualitative and budget-friendly coffee that is quick to make and that saves time for busy people. |
The analysis based on the 5W method not only makes it possible to see the potential target audience but also to build a customer avatar and understand what problems customers face and what solutions can be offered.
How do you create your customer avatar?
After your target audience has been determined, it is important to make your customer avatar. It is a must for promoting your product and developing your advertising campaign. It allows creating your USP (Unique Selling Proposition), calculating the benefits and levers, finding out customers’ problems, and offering a solution.

The customer avatar is based on the key attributes of the target audience that were researched earlier. Before this, the following questions should be answered:
- Who is your client?
How old are your customers, where do they live, what is their marital status and how many kids do they have?
- How and how much money do they earn?
Their profession and level of income.
- How do they spend money?
Do they make purchases easily, what can they afford and what do they spend money on?
- What are their interests?
Interests, hobbies, and other activities apart from work.
- What is their life philosophy?
What are their different beliefs and stereotypes including religious, political, and nutritious views, etc.?
- What are their problems and pain points?
What worries them and occupies their thoughts? What prevents them from living the life they want?
- How do they spend time online?
On what social networks do they have accounts? What is their aim and what content are they interested in there?
By answering all these questions you will get an avatar of a typical representative of your target audience.
Example
Say, the company produces re-usable cups for hot beverages out of natural environmentally-friendly materials. The price is above the market rate due to the high price for raw materials and qualitative packaging. A lot of money is also spent on promotion and making advertising videos, and it is also included in the final price of the product. The brand collaborates with popular bloggers, that are conscientious and call to living an eco-friendly life.
The target audience of the brand is young men and women aged 18-35 who have a degree and above-average income. They often drink coffee and go out to have breakfast, but sometimes take meals and drinks from home. They live an active lifestyle, are interested in today’s world, and are concerned about the environment. They don’t waste their money and rarely make impulsive purchases. It is important for them that the brand shares its values and is truly loyal to companies they like. They spend a lot of time on social media, where they find new information. They’re receptive to their friends’ and influencers’ recommendations.

It looks like the initial avatar of the target audience is made correctly. But eco-friendly dinnerware and conscientiousness are becoming more popular. Moreover, people join up with the movement, both teenagers younger than 18 and elderly people. Thus, the brand needs to expand its target audience and make more avatars of typical clients. It should be both teenagers, who are actively interested in ecology, and elderly people, who live active social lives and follow trends.
Thus, every business should constantly review, expand, and supplement the customer avatar, follow trends of the industry, and track the influence of external factors.
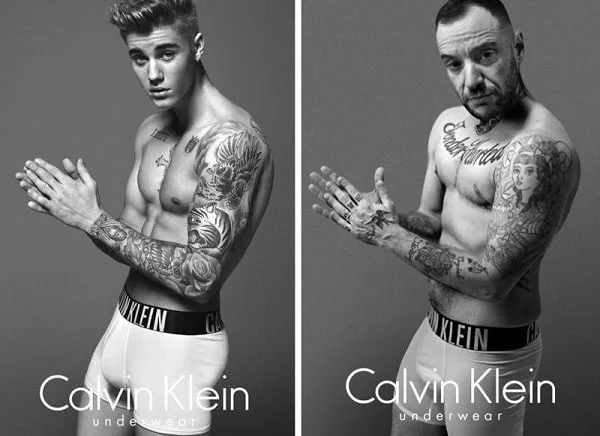
Here are some examples of adverts that are based on the customer avatar.



Where to look for information about your target audience
It is not enough just to determine your target audience and make your customer avatar. You also need to know where to look for those people and how to attract them. It is the marketers’ task to research the audience and divide it into segments.
There are open sources where information can be found. For example, published research, analytical websites, and trends, experts’ opinions, etc. Also, potential customers can be asked to take an opinion poll and take part in tests.
Where to look for your target audience:
1. Social media
This is one of the best places to look for your audience. Search in thematic communities and analyzing people’s interests will allow you understanding your target audience and gathering all those people for your targeted advertising.
On social networks, people readily talk about their life, preferences, and interests. The geolocation allows tracking places those people visit and where they normally go as well as what they watch online and what people they follow. All this information forms the basis of the segmentation process.
2. E-mail marketing
Professional marketers can turn e-mails into a powerful tool that allows you to manage your target audience. Special forms on websites, blogs, and social networks are used to collect the addresses of potentially interested customers. Don’t forget about collecting information offline: ask your customers to fill forms in exchange for a discount card or a small gift.
3. Search engines
With good search engine optimization (SEO), the target audience will find you simply by putting in search requests. You can set up advertising in a way that a person will be shown a promo banner of your product based on their previous requests or websites of the competitors they have viewed.
4. Blogs
Personal blogs and thematic communities practically are the ready-made representation of the target audience that is already segmented according to interests.
It also includes promotion through famous bloggers. Normally, they already have their active audience that satisfies your requirements. The most important thing here is to choose the right blogger and integrate your product in the right way.
5. Competitors
There are companies whose activities are similar to yours. You can research their target audience and “borrow” it for your campaign. Check who follows your competitor’s groups on social networks, what the company offers, and who their client is. Think about how you can make them interested.
| To create your main target audience profile and to single out minor audiences, try using different channels for information search. Place an application form on your website, suggest that your clients take part in polls, and find out who uses the services of your competitors. |
Tips on how to work with your target audience
1. Determine your target audience before launching your business
Allocate some time for doing market research and seek help from professional marketers.
2. Use all available sources to look for information about your target audience —
networks, open research, social inquiries, and other sources that might help find the target audience and understand what it needs.
3. Create your customer avatar and renew it from time to time
That is how you will understand who your customers are and build communication with them. Sometimes it is important to go back to the customer avatar and ask yourself the same questions depending on the situation in the world around you.
4. Develop your offers and advertising campaigns particularly for your target audience.
All external communication should be aimed at your potential clients. It should share their values and help solve their problems.
5. Check out your competitors
Analyze the market. Have a look at how other brands in your industry communicate with their customers and what they offer. Take note of their mistakes. If it is possible, use them to your advantage by offering customers something that your competitors do not have.
6. Follow trends
Everything that happens to people affects their lives and their purchase decisions. Try to keep up with the times and make your offers correspond to the current demands of your customers.
7. Collect your customers’ contact details.
Try to get a mobile phone and an e-mail address of a person. But do it in a non-intrusive way not to scare a person away. And observe the data protection laws of your country.
8. Listen to your audience
Don’t ignore feedback. Especially, negative feedback. There is always time to adjust your target audience, review your USP, and improve your marketing campaign.
If you determine your audience correctly and hit the target, you have already won half the battle of any business. It is worth spending time on. Know your audience. Love your clients.








